Description
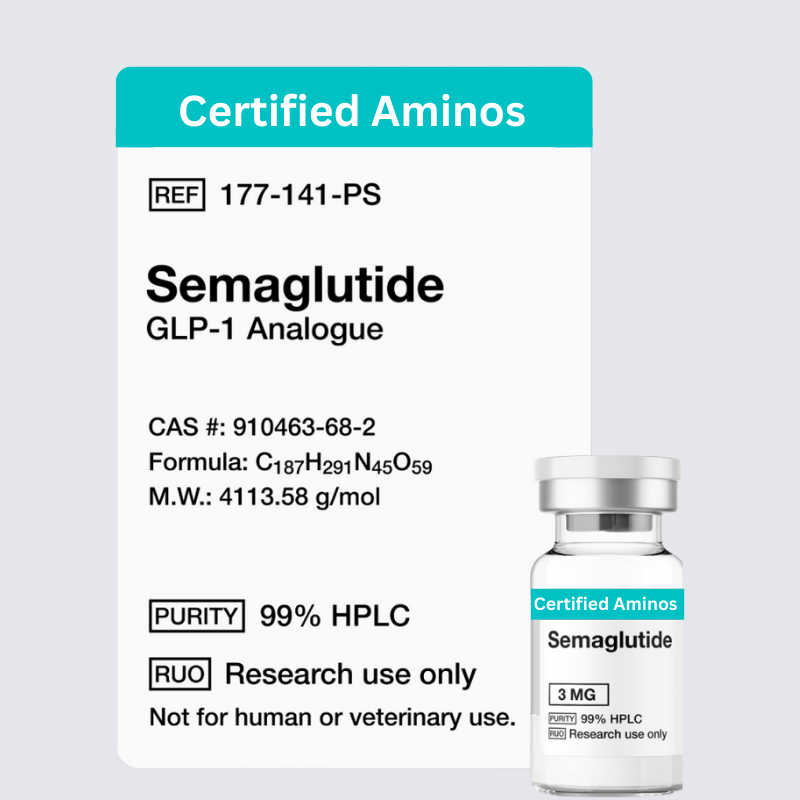
Semaglutide (GLP-1 Analogue) 3mg – Research Peptide
Semaglutide is a research peptide modeled after GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1), a naturally occurring hormone in the body. This GLP-1 analogue has been widely studied for its role in blood sugar regulation, appetite control, and potential protective effects on the heart, brain, and other organs.
What Is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a synthetic version of GLP-1 designed to last longer in the body. In laboratory studies, it has been shown to:
-
Lower blood glucose levels
-
Enhance insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner
-
Reduce appetite by slowing down gastric emptying
-
Potentially improve functions of the heart, liver, lungs, and brain
Researchers are also exploring its effects on neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, thanks to its impact on reducing amyloid-beta plaque buildup in the brain.
Understanding GLP-1 and Its Functions
GLP-1 is a short peptide hormone made up of 30–31 amino acids. It plays a key role in regulating blood sugar by:
-
Stimulating insulin secretion
-
Suppressing glucagon release
-
Protecting insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas
GLP-1 also slows digestion, which can lead to reduced hunger and food intake. In various studies, it has shown promise in supporting weight management and improving insulin sensitivity.
Semaglutide and Appetite Regulation
In animal studies, GLP-1 and its analogues, including Semaglutide, have been shown to reduce food intake and support weight loss. This effect is believed to come from increased satiety and delayed gastric emptying. Consistent use in these models led to gradual weight loss and improved metabolic markers like HbA1c levels—a key indicator of blood sugar control.
Cardiovascular and Metabolic Research
GLP-1 receptors are present in heart tissue, where they may help:
-
Improve heart function
-
Reduce blood pressure
-
Enhance glucose uptake in heart muscle during stress or injury
These effects suggest a possible protective role during events like heart attacks, where maintaining energy supply to cardiac tissue is crucial.
Brain and Cognitive Support
Preliminary studies have shown that GLP-1 may support brain health by:
-
Enhancing memory and learning
-
Promoting neuron survival
-
Reducing amyloid-beta buildup—associated with Alzheimer’s disease
These neuroprotective effects have sparked interest in the potential of GLP-1 analogues as therapeutic candidates for cognitive decline and neurodegenerative conditions.
Technical Details
-
Sequence: HXEGTFTSOVSSYLEGQAAK-CH.staric diacid-EFLAWLVRGRG
-
Molecular Formula: C187H291N45O59
-
Molecular Weight: 4113.58 g/mol
-
CAS Number: 910463-68-2
-
Synonyms: Semaglutide, Ozempic, Rybelsus, NN9635
-
PubChem CID: 56843331
Important Research Notes
GLP-1’s ability to boost insulin release and protect pancreatic beta cells makes it a prime focus in diabetes-related studies. In preclinical trials, GLP-1 has even shown the ability to promote beta cell growth while reducing their destruction by inflammatory signals—critical in type 1 and type 2 diabetes research.
In addition to metabolic and cardiovascular benefits, GLP-1 is being closely examined for its possible role in reducing the progression of Alzheimer’s and similar neurodegenerative conditions.
For Research Use Only
This product is intended strictly for laboratory research and in-vitro studies. It is not approved for human or animal use and is not a medication. Please ensure proper licensing and compliance before ordering.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.